For new players of CRUMB, this guide will show you a simple circuit for new comers that don’t know how to build the circuit on the breadboard
Overview
This is a simple walk-through guide for the beginner to learn how to use the breadboard to build a circuit based on your design. This guide will include:
- Understand the breadboard
- Preparation
- Wire and components
- Power on
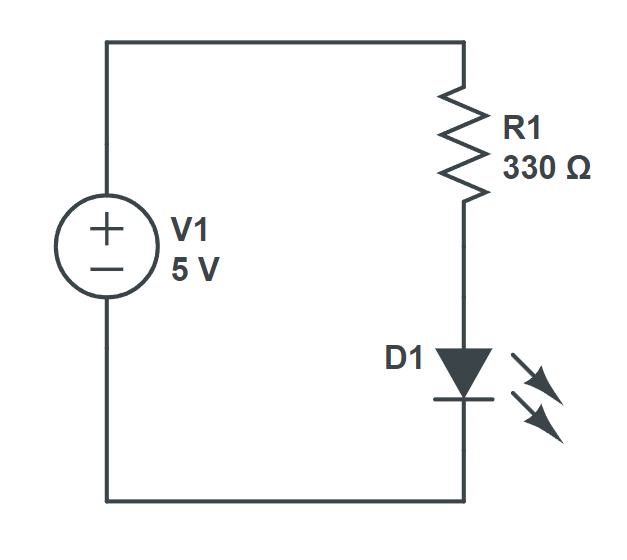
The circuit diagram for this guide is:
Understand the breadboard
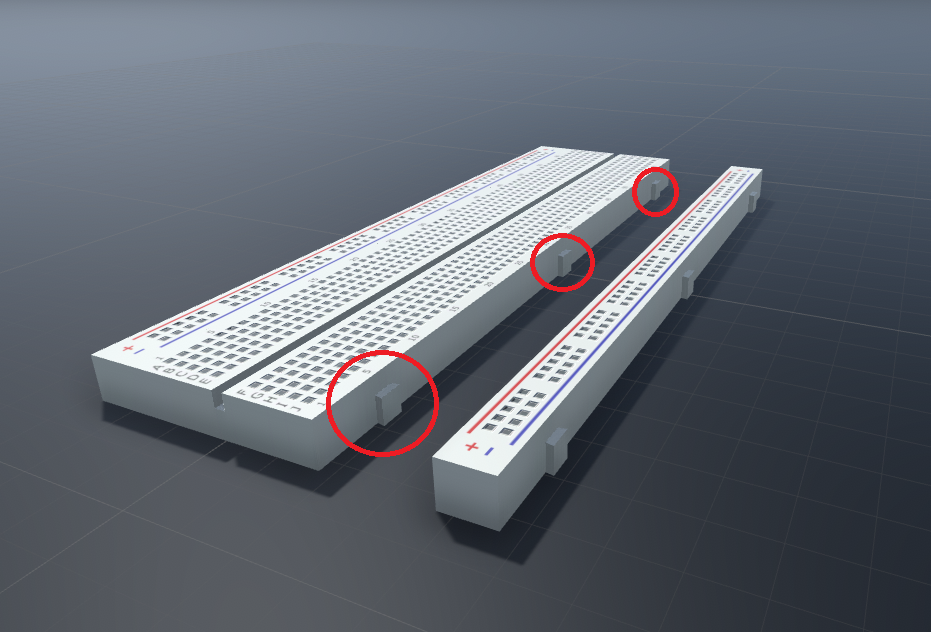
Breadboard is very commonly used in the lab for building the temporary circuit. By using a breadboard, soldering is not needed and is easier for the user to change the connections very quickly.The first thing that we need to do is to attach the power rail to the top and bottom of the breadboard.
After attaching the power rail the breadboard should look like this.
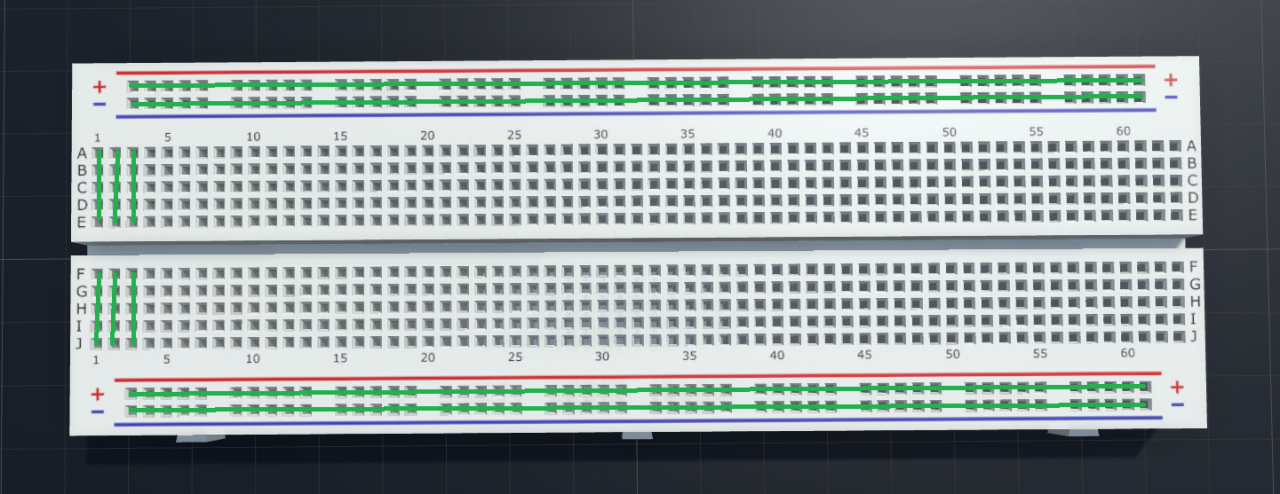
In the diagram above, you can see some green lines that represent the common connection (row and column).
For example, the wire/connections inserted in A1 is electrically connected to B1, C1, D1, E1. This applies to the power rails as well.

Preparation
There are a few preparation steps we will usually take before start making connections. The very first thing to do is to connect the power rails.
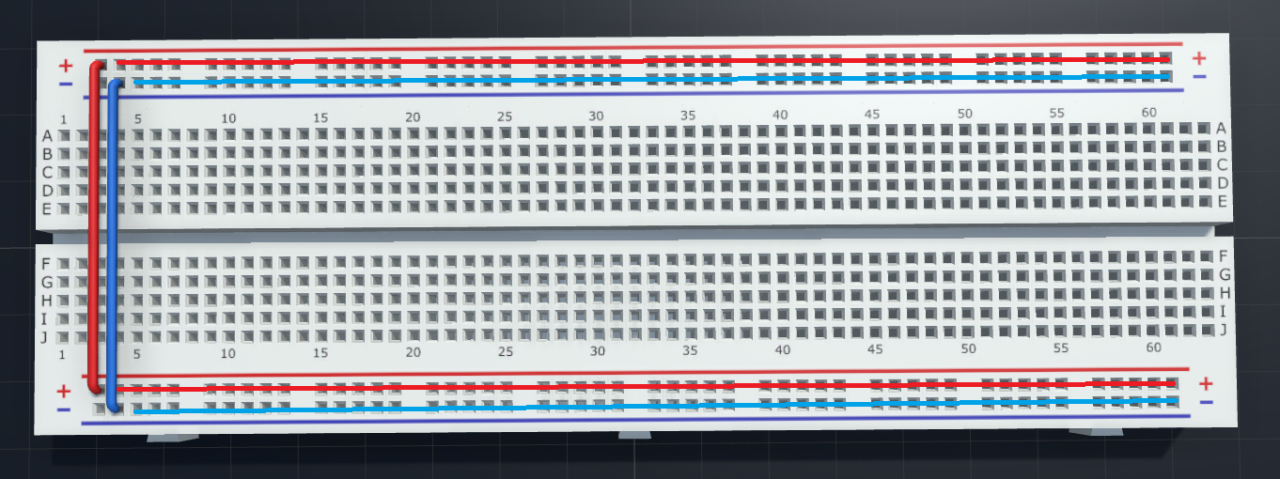
As you can see the (+) rail on top is connected to the bottom (+) rail. Same thing applies to the (-) rails. This is much easier for us to make connections and easier for the wire managements when circuit is getting more and more complicated.
Secondly, If we have a lot of components, we need to plan the placement of the components. This is very simple but crucial step to ensure minimum wire crossing on the breadboard. But in this guide only a few wires are needed so it is not very significant.
Wire and components placement
Firstly, we look back the circuit diagram.

The important thing we need to beware is the polarity of the components.
As you can see in this circuit diagram, the (+) polarity of the power source is connected to one of the terminals of the 330ohm resistor.
Then another terminal of the resistor is connected to the anode (which is also refer to the positive terminal) of the LED. The cathode (negative terminal) of the LED is connected to the (-) terminal of the power source.
Resistor
So we can now place the resistor first onto the breadboard. In this case, I place the resistor in hole E12 and F12. The resistance of the resistor is set as 330 ohm.
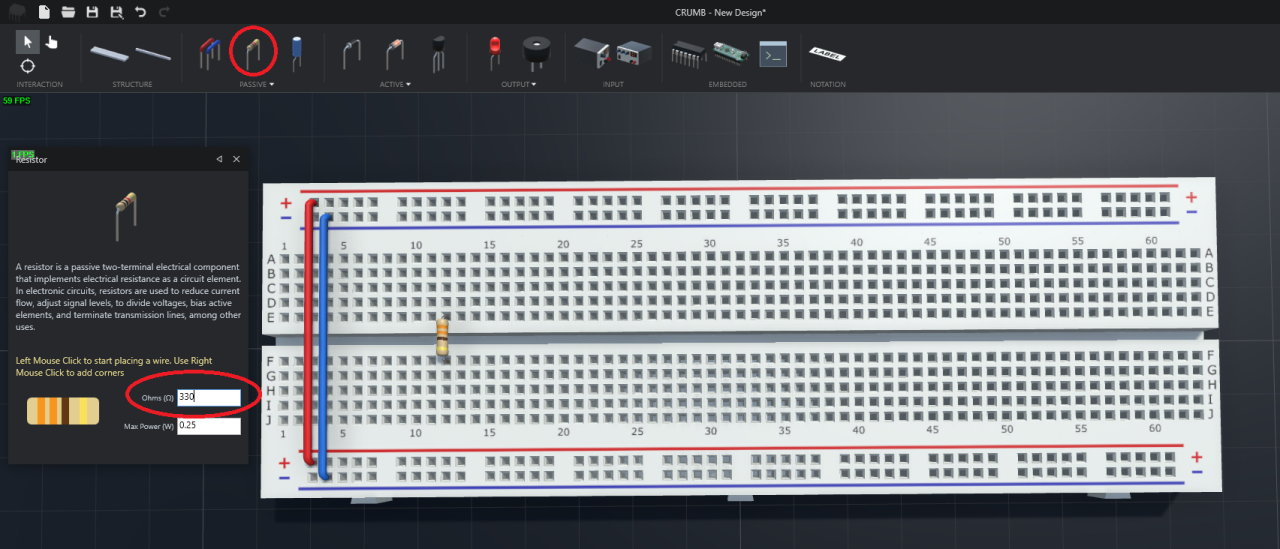
Next, I place the LED in hole F18 for anode (+) and E18 for cathode (-).
IMPORTANT: Please look carefully for the anode (+) and cathode (-) pins of the LED !
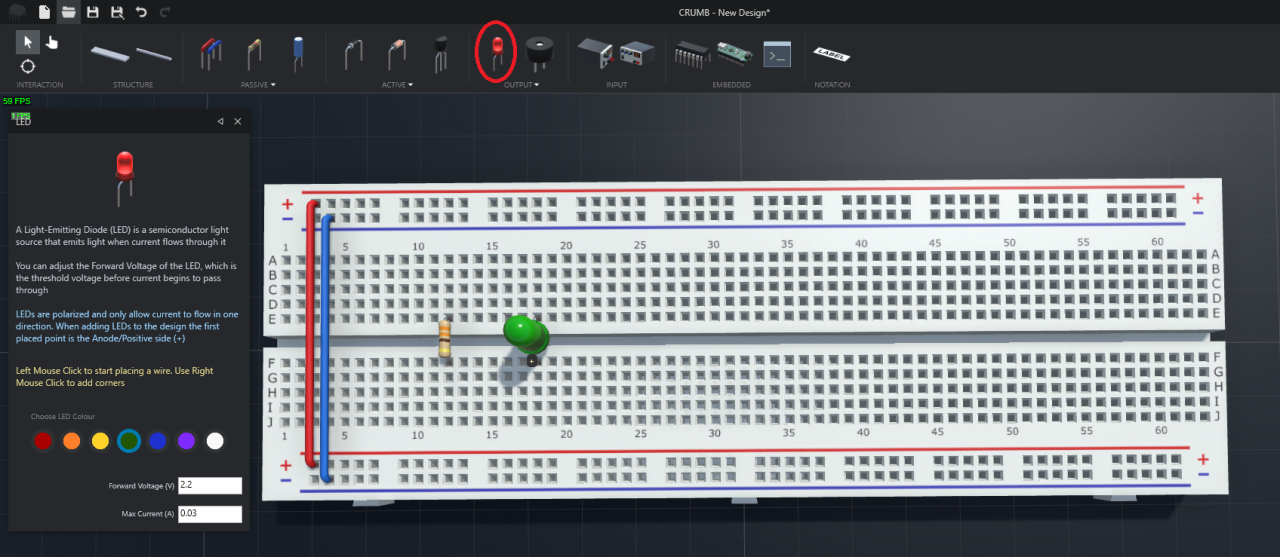
Lastly, we need to connect each of the components (resistor and LED) to form a closed circuit.
You can compare the diagram below with the circuit diagram to understand better.

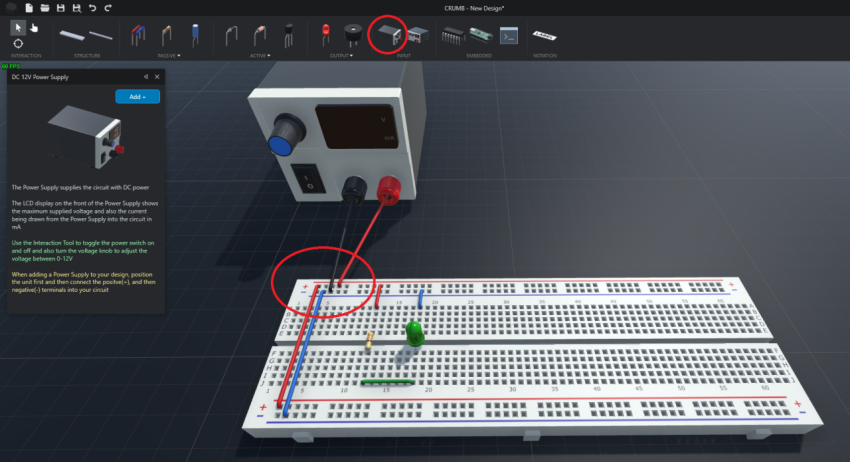
Power On
Lastly, we need power supply to electrically turn on the the circuit. Based on the diagram below, you can see that the red terminal of the power supply is connected to the (+) power rail and black terminal is connected to the (-) power rail.
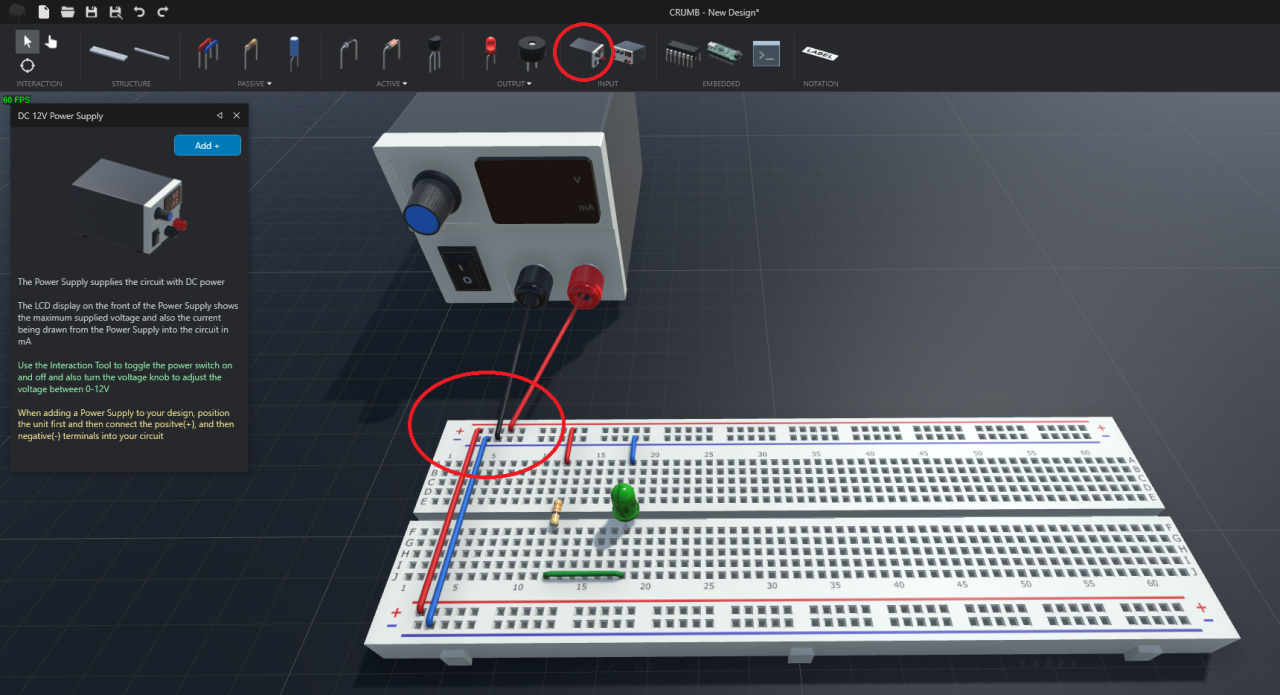
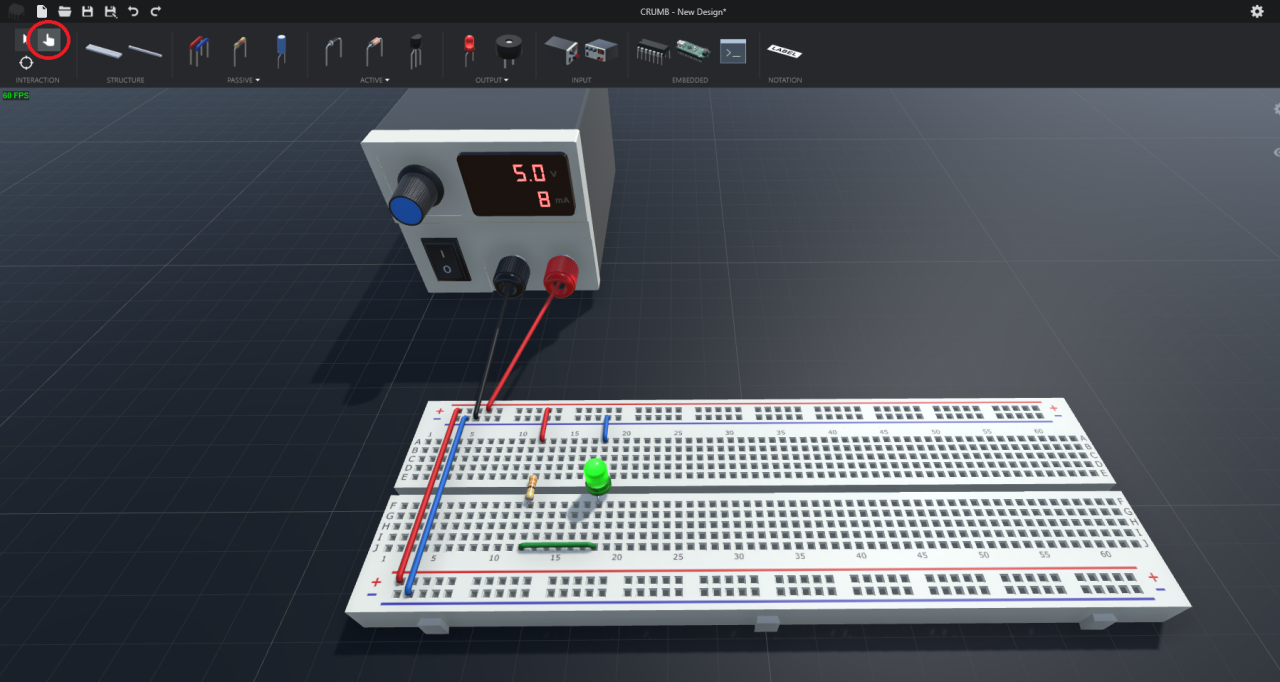
Lastly, we can switch to the Interact tool and turn on the power supply.
One has to download Steam to be able to buy and use this software!??? Thinkercad now wants you to log your phone into their servers!?? That’s all becoming just too ridiculous! Your money is not enough anymore they all want your data on top of it today! I miss the times when one purchased software, installed it, and just used it!